Discovering
the Polymers
The world of polymers is complex and fascinating.Educating is one of IPPR’s missions, which is why you will find below a detailed analysis of the complex world of polymers, in terms of materials, transformation processes and application sectors. Indeed, there is something for everyone.
Plastic: families and materials
From a chemical viewpoint, plastics are generally obtained through the polymerisation of a number of basic molecules (monomers) to form long chains. We speak of homopolymers if a single type of monomer is used, copolymers if two or more different monomers are used, and polymer alloys if the material is obtained by mixing two monomers that polymerise without combining chemically.
To this polymer base, various substances (called “fillers”) are then added depending on the application the plastic is intended for. These substances can be plasticisers, dyes, anti-oxidants, lubricants and other special components that give the finished plastic material the desired properties of workability, appearance and strength.
The advantageous characteristics of plastics over metallic and non-metallic materials include greater ease of processing, cost-effectiveness, colourability, acoustic, thermal, electrical and mechanical (vibration) insulation, corrosion resistance and chemical inertness, as well as water-repellence and invulnerability to mould, fungus and bacteria.
An analysis of plastic families and materials is given below.
Thermoplastics and Thermosetting Plastics
Thermoplastics
Thermosetting Plastics
Sono un gruppo di materie plastiche che, dopo una fase iniziale di rammollimento dovute al […]
ACRILONITRILE-BUTADIENE-STIRENE – ABS
Ottenuto per copolimerizzazione di acrilonitrile, butadiene e stirene.
[…]
POLIESTERI INSATURI – UP
Le resine poliestere insature si ottengono per esterificazione di una miscela di un acido […]
POLIACETALI – POM
Ottenuti per polimerizzazione di aldeide formica. Utilizzato prevalentemente nella […]
POLIURETANI – PU
POLIAMMIDI – PA
Ottenuti dalla reazione fra diammine e acidi bibasici o fra lattami e amminoacidi. […]
RESINE ALCHIDICHE
POLIBUTILENTEREFTALATO – PBT
Ottenuto per condensazione dell’acido tereftalico con butilenglicole. E’ […]
RESINE ALLILICHE – DAP
Ottenute mediante esterificazione dell’alcool insaturo allilico con acidi ftalici. […]
POLICARBONATO – PC
Ottenuto per reazione di bisfenolo e fosgene. Utilizzato per manufatti trasparenti, caschi […]
RESINE EPOSSIDICHE – EP
Ottenute per condensazione di bisfenolo e epicloridrina. Utilizzata nella produzione di […]
POLIFENILENOSSIDO – PPO
E’ un polimero di policondensazione di tipo polietere aromatico del 2,6 metilfenolo. […]
RESINE FENOLICHE - FENOPLASTI – PF
Ottenute per condensazione di fenolo e formaldeide. Utilizzata nella produzione di […]
POLIETILENE o POLITENE – PE
Scoperto da Gibson e Fawcett nel 1935 e ottenuto per polimerizzazione dell’etilene. […]
RESINE FURANICHE
POLIFENILENSOLFURO – PPS
Ottenuto trattando il paradicloro-benzene con il solfuro di sodio in presenza di solventi. […]
RESINE MELAMINICHE – MF
POLIETILENTEREFTALATO – PET
Ottenuto per condensazione dell’acido tereftalico con glicoletilenico. Utilizzato per […]
RESINE UREICHE – UR
POLIISOBUTILENE – PIB
Il poliisobutilene è un polimero saturo termoplastico. E’ caratterizzato da […]
OLITETRAFLUOROETILENE - PTFE (Teflon)
POLIVINILIDENCLORURO – PVDC
Ottenuto per polimerizzazione del cloruro di polivinilidene (policloruro di vinilidene). […]
POLIMETILMETACRILATO – PMMA
Ottenuto per polimerizzazione dell’acido metacrilico. Viene utilizzato per la […]
POLIVINILIDENCLORURO CLORURATO – CPVDC
Ottenuto per clorurazione del cloruro di polivinile. E’ caratterizzato da una […]
POLIPROPILENE – PP
Ottenuto per polimerizzazione del propilene. Utilizzato per la produzione di componenti per […]
POLIVINILIDENFLUORURO – PVDF
Ottenuto per polimerizzazione del fluoruro di vinilidene, è caratterizzato da […]
POLISOLFONI – PSU
Ottenuti per reazione fra difenileteri e difenilsolfoni. Utilizzato per apparecchiature che […]
TERPOLIMERO METILMETACRILATO BUTADIENE STIRENE – MBS
Ottenuto per polimerizzazione e innesto di metilmetacrilato, sul copolimero butadiene […]
POLISTIRENE o POLISTIROLO – PS
Ottenuto dalla polimerizzazione dello stirene. Nelle versioni cristallo o antiurto viene […]
POLISTIRENE ESPANSO – EPS
Ottenuto dalla polimerizzazione dello stirene in presenza di un agente espandente. Una […]
TERPOLIMERO ACRILONITRILE - STIRENE - ESTERE ACRILICO – ASA
Ottenuto per polimerizzazione e innesto: un elastomero acrilico disciolto in stirene e […]
TERPOLIMERO ACRILONITRILE - STIRENE - ESTERE ACRILICO – ASA
Ottenuto per polimerizzazione e innesto: un elastomero acrilico disciolto in stirene e […]
POLIVINILACETATI – PVA
Ottenuti per polimerizzazione dell’acetato di vinile. Utilizzati per la produzione di […]
TERPOLIMERO METILMETACRILATO BUTADIENE STIRENE – MBS
Ottenuto per polimerizzazione e innesto di metilmetacrilato, sul copolimero butadiene […]
POLIVINILCLORURO – PVC
Ottenuto per polimerizzazione del cloruro di vinile. Prodotto industrialmente, dal 1930, il […]
ACETATO DI CELLULOSA – CA
Ottenuto per reazione di cellulosa con anidride acetica in presenza di solventi e […]
COPOLIMERO STIRENE-ACRILONITRILE – SAN
Ottenuto per copolimerizzazione di stirene ed acrilonitrile. Viene utilizzato in […]
ETILENVINIL ACETATO – EVA
Ottenuto per co-polimerizzazione dell’etilene con acetato di vinile. Le […]
I processi di trasformazione
Ottenuto per condensazione dell’acido tereftalico con butilenglicole
Calandratura
Estrusione
Stampaggio
Soffiaggio
Application Sectors
On account of their characteristics and properties, plastics can be used in countless applications. Developments in production, processing machines and processing methods have made it possible to attain excellent results in many different application sectors. Theoretically, plastics can be developed to obtain virtually any combination of properties to suit any desired application.
Because of these properties, plastics are increasingly used in the following areas of application:
- Packaging
- Building industry
- Mobility and transport
- Healthcare
- Electronics
- Agriculture
- Sport and Entertainment

Fonte: PlasticsEurope the facts 2019
The figure above shows a breakdown of plastic materials by application.
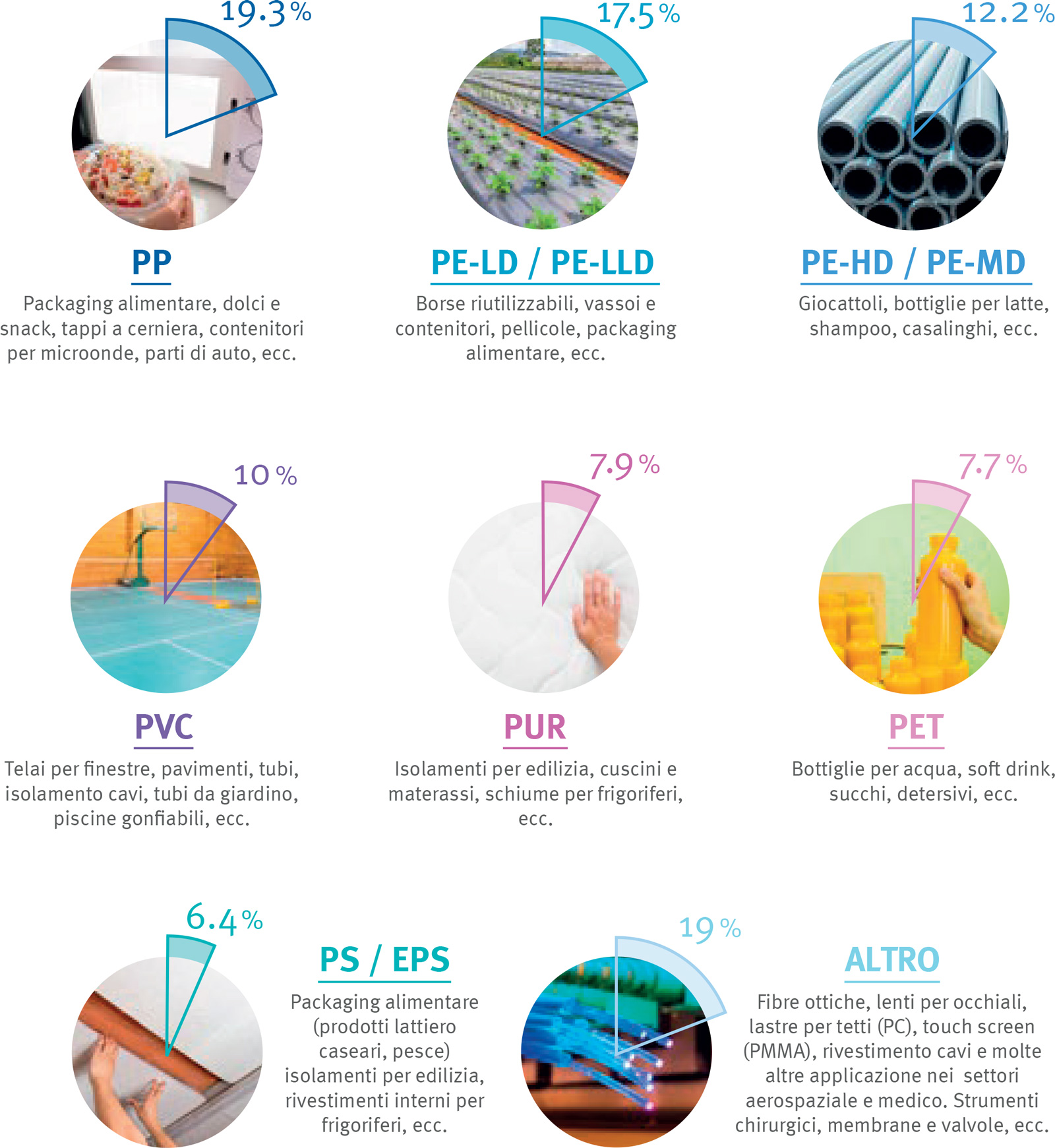
Fonte: PlasticsEurope the facts 2019
The previous figure describes the applications of the main polymers and their significance as a percentage of the quantities processed in Europe.
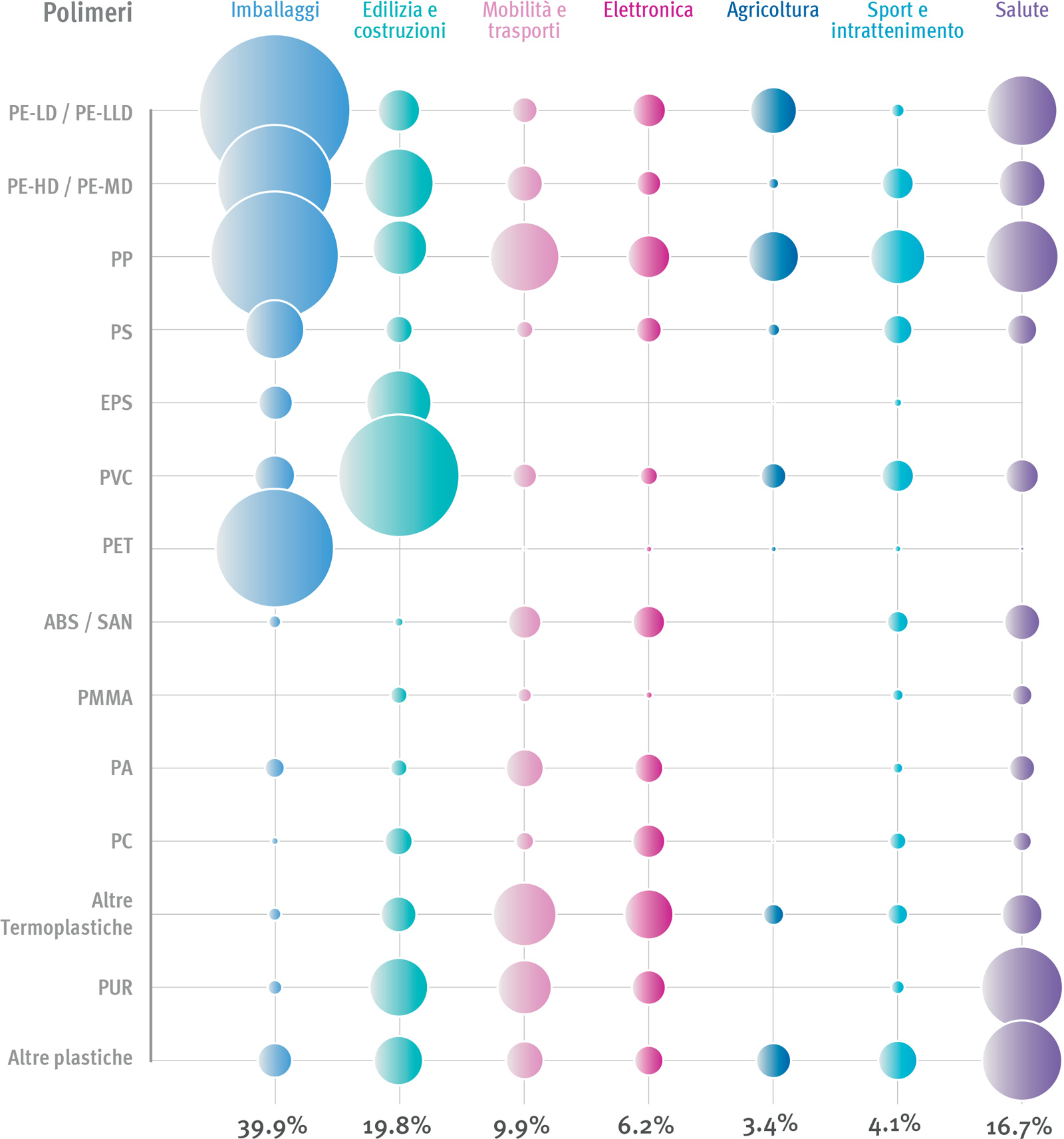
Fonte: PlasticsEurope the facts 2019
The previous figure shows the significance of each polymer for each individual application and for different applications.

